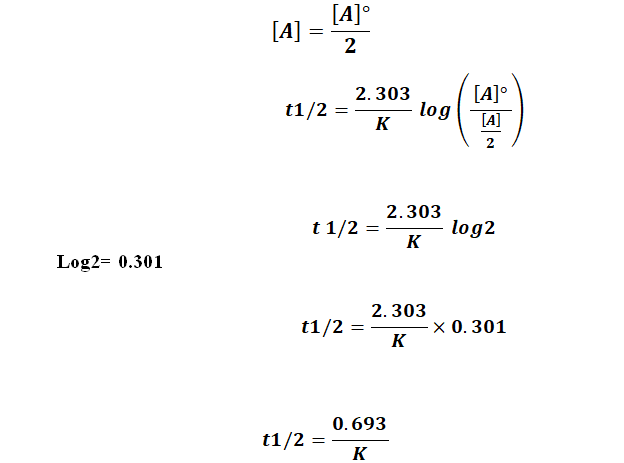half life formula for first order reaction
Solving for the half-life we obtain the simple relation. The half-life formula for a reaction depends upon the order of a reaction.
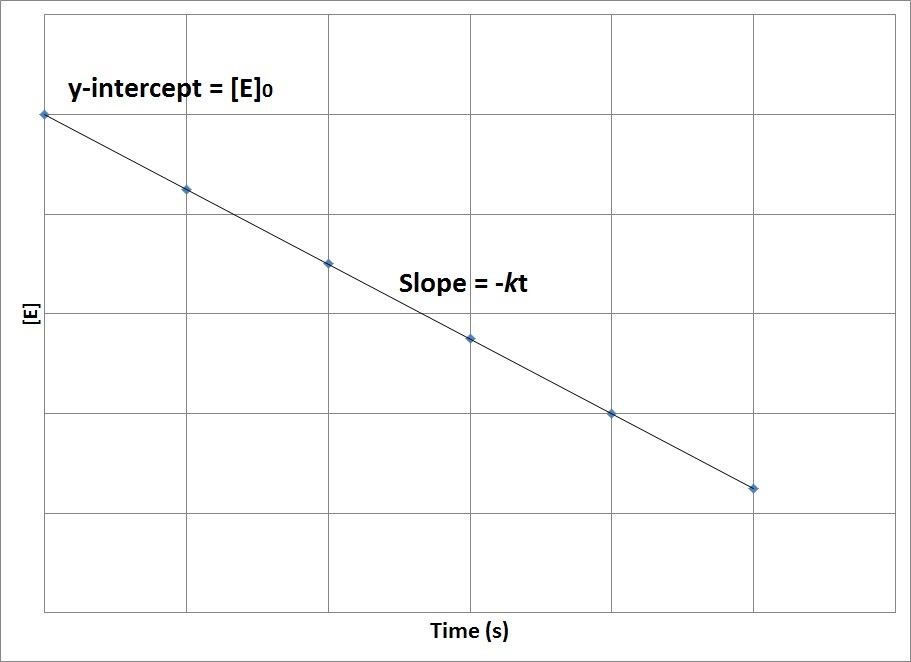
Concentration Time Relationships Integrated Rate Laws Introductory Chemistry 1st Canadian Edition
We can derive an equation for determining the half-life of a first-order reaction from the alternate form of the integrated rate law as follows.

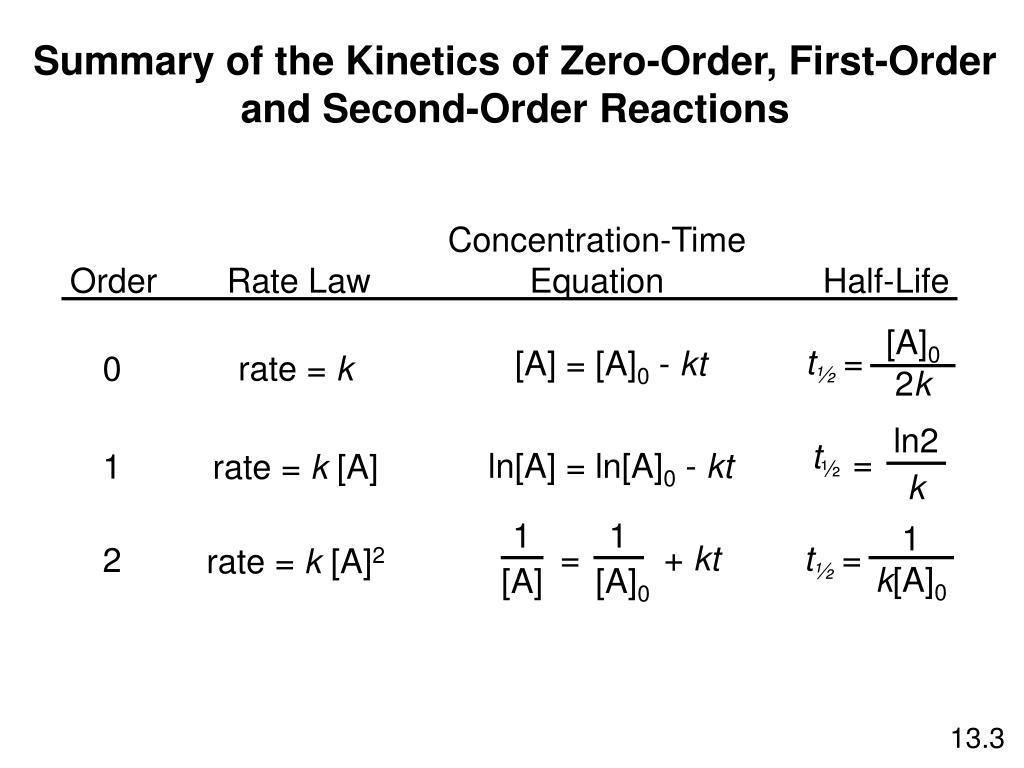
. The half-life t12 is the. For a zero-order reaction the mathematical expression that can be employed to determine the half-life is. For a zero-order reaction the half-life equation is given as.
The half-life of a second-order reaction is. 1 R t 1 R o k t. The half-life formula for various reactions is given below.
For a general reaction. The half-life of a second-order reaction is. We know that at the half-life time eqt_12 eq the concentration of the reactant will.
The half-life of a first-order reaction is given as t 12 0693k. Using the concentration-time equation for a second-order reaction we can solve for half-life. The half-life of a reaction is the time required for a reactant to reach one-half its initial concentration or pressure.
Since at half-life the concentration of the reactant reduces to half t t12 Half-life and R. How to calculate Half Life period of first order reaction using this online calculator. Half life formula for First order reaction.
The half-life of a chemical reaction regardless of its order is simply the time needed for half of an initial concentration of a reactant to be consumed by the reaction. For a first-order reaction the half-life is given by. The rate constant of a second-order equation expressed in integrated form is.
The order of the reaction or enough information to determine it. Now a first - order. The mathematical expression that can be employed to determine the half-life for a zero-order reaction is t12 R 02k.
A zero order reaction implies that the rate of the reaction does not depend on the concentration of the reactant. For a first zero order. The decay of carbon-14 is a first-order reaction so the half-life of carbon-14 was calculated using that equation.
What is the expression for Half-Life of a First Order ReactionHere I derive it from the integrated rate lawThe answer is t ln 2 kAsk me questions. If we set the time t equal. The half-life of a zero-order reaction the formula is given as t 12 R02k.
238 t 1 2 ln 2 k 0693 k. The half-life of a zero-order reaction the formula is given as t 12 R 0 2k. TRA3C LO TRA3C5 EK Transcript.
The rate constant k for the reaction or enough information to determine it. The formula for determining an objects age using carbon dating is. The half-life of a first-order reaction is a constant that is related to the rate constant for the reaction.
The half-life of a first-order reaction is given as t 12 0693k. In some cases we need to know the initial. To use this online calculator for Half Life period of first order reaction enter Rate Constant K h and hit.
This indicates that the half-life of a first-order reaction is a constant. What is the formula for half-life of a drug.

Rate Equation And Order Of Reaction

Calculate The Half Life Of A First Order Reaction From Their Rate Constants Given Below A 200 S 1 B 2 Min 1 C 4 Year 1
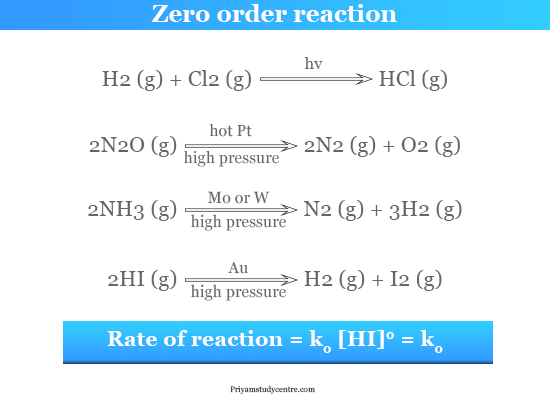
Zero Order Reaction Definition Examples Formula
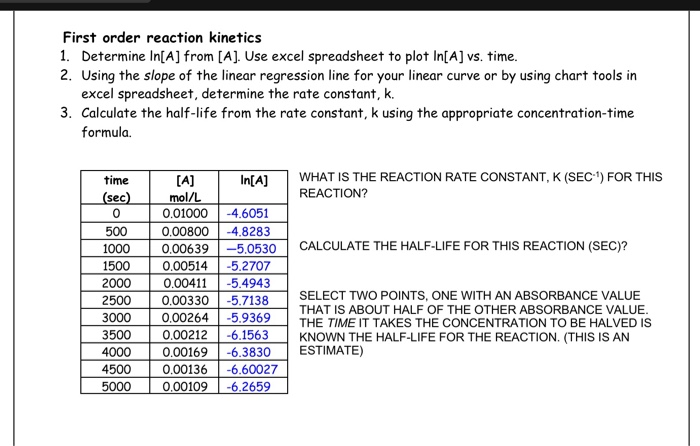
Solved First Order Reaction Kinetics 1 Determine In A From Chegg Com

How To Calculate Half Life Of A Second Order Reaction Chemistry Study Com

Solved Please Help With Q1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Amp Chegg Com
A Derive The General Form Of The Expression For The Half Life Of A First Order Reaction Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
2 3 First Order Reactions Chemistry Libretexts

Half Life Of A First Order Reaction Video Khan Academy

Physical Chemistry Formula For Rate Constant For The First Order Reaction Chemistry Stack Exchange
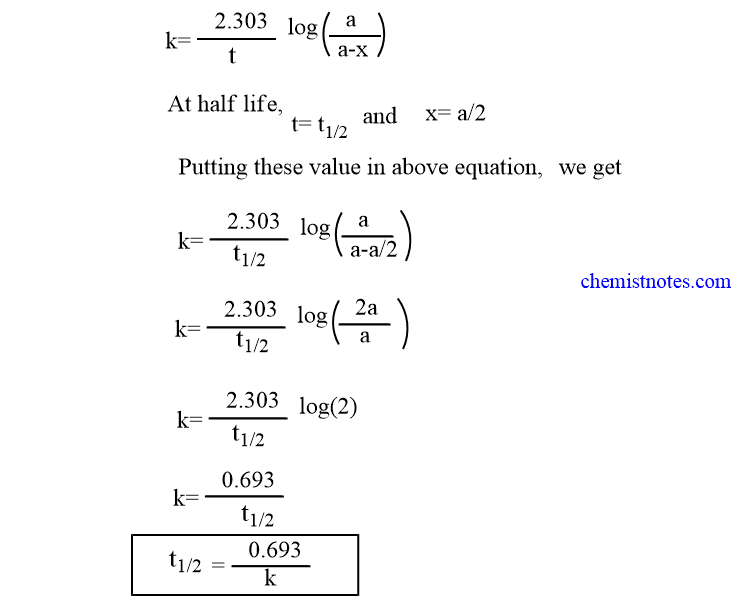
First Order Reaction Definition Example Half Life Period Chemistry Notes

5 Ways To Calculate Half Life Wikihow

Half Life Of First Order Reaction Youtube
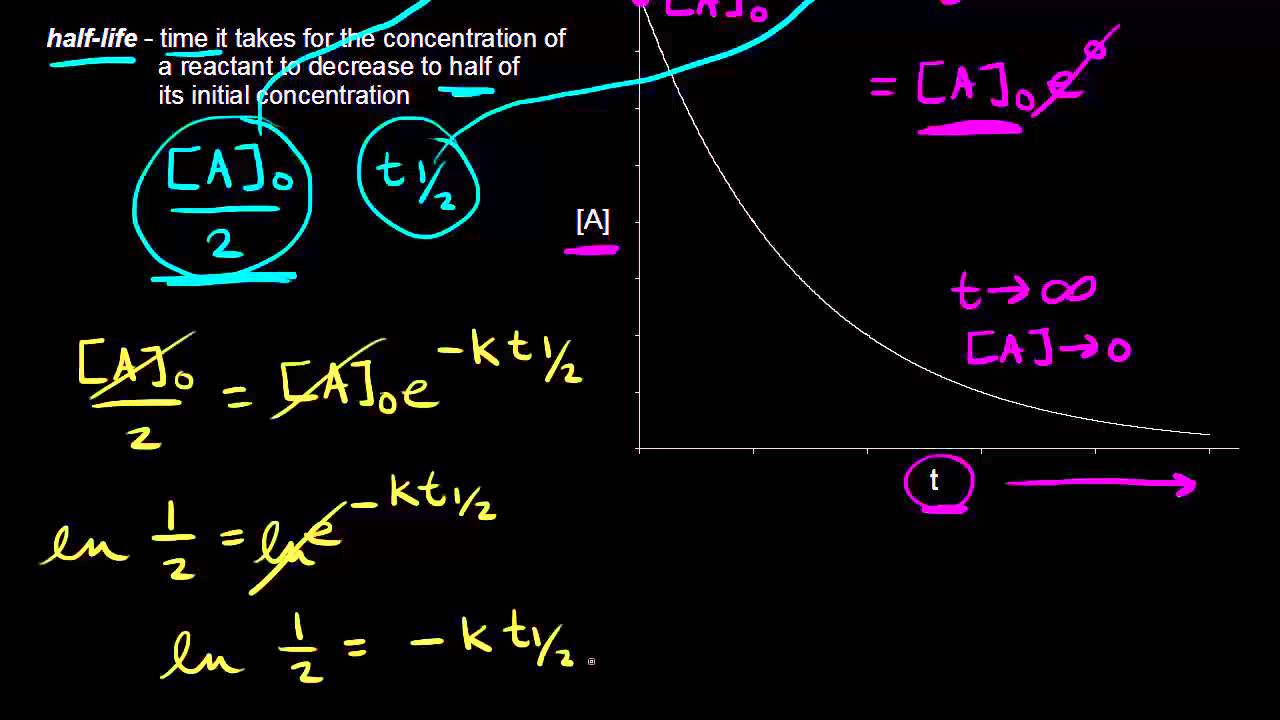
Half Life Of A First Order Reaction Video Khan Academy

Calculate The Half Life Of A First Order Reaction From Their Rate Constants Given Below